This is a knockout-validated antibody summary, based on the publication "Increased hepatic receptor interacting protein kinase 3 expression due to impaired proteasomal functions contributes to alcohol-induced steatosis and liver injury", as cited below [1]. Labome curates formal publications to compile a list of antibodies with unambiguous specificity within Validated Antibody Database (VAD).
Rabbit polyclonal
Company: ProSci Inc
Antibody: RIP3
Catalog number: 2283
Summary: Rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against a 14 residue peptide corresponding to a sequence within the C-terminal region of mouse RIP3.
Supplier recommended for WB, IF, IHC and elisa.
Peptide affinity-purified.
Reacts with human, mouse and rat RIP3.
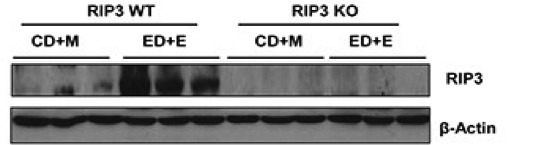
Western blot
Lysates of liver from wilf-type and RIP3 knockout mice. Wild-type human and mouse hepatocytes.
Anti-RIP3 antibody.
HRP-conjugated secondary antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories).
SuperSignal West Pico chemiluminescence reagent.
If the antibody described in this summary is a polyclonal antibody, since polyclonal antibodies are of limited quantity, please inquire the supplier whether any current polyclonal antibody with the same catalog number is exactly the same as the one described in this summary. Sometimes, different bleeds or different animals are used, usually with a different lot number. In such cases, the result in this summary may not apply to the new antibody with the same catalog number.
- product
