This is a knockout-validated antibody summary, based on the publication "The NEMO adaptor bridges the nuclear factor-kappaB and interferon regulatory factor signaling pathway", as cited below [1]. Labome curates formal publications to compile a list of antibodies with unambiguous specificity within Validated Antibody Database (VAD).
Mouse monoclonal
Company: Cell Signaling Systems
Antibody: NEMO (IKKgamma)
Catalog number: 2695, Clone DA10-12
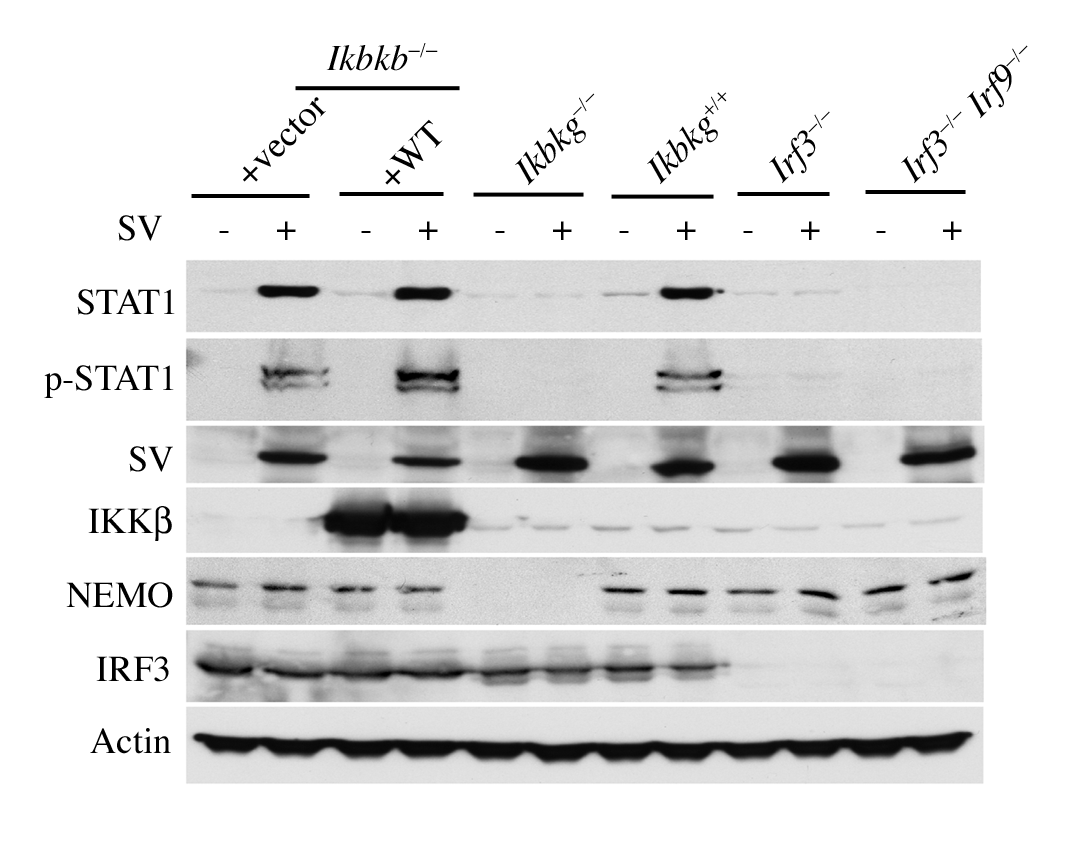
Summary: Mouse monoclonal antibody raised against full-length GST-tagged human NEMO (IKKgamma). Supplier recommended for WB. Reacts with human and rat NEMO.
Western blot
Lysates of MEFs from wild-type and NEMO KO (Ikbkg -/-) animals.
PBS containing 5% milk powder and 0/1% Tween 20.
Anti-NEMO antibody at 1μg/ml in PBS containing 5% milk powder.
HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG (Amersham) at 1:3000 dilution in blocking buffer.
ECL reagent.
If the antibody described in this summary is a polyclonal antibody, since polyclonal antibodies are of limited quantity, please inquire the supplier whether any current polyclonal antibody with the same catalog number is exactly the same as the one described in this summary. Sometimes, different bleeds or different animals are used, usually with a different lot number. In such cases, the result in this summary may not apply to the new antibody with the same catalog number.
- Zhao T, Yang L, Sun Q, Arguello M, Ballard D, Hiscott J, et al. The NEMO adaptor bridges the nuclear factor-kappaB and interferon regulatory factor signaling pathways. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:592-600 pubmed
- If you are aware of any publication with knockout studies validating a monoclonal or recombinant antibody, either purchased from a supplier or developed by the author(s), please notify us through feedback.
- product
