This is a knockout-validated antibody summary, based on the publication "Efficient Generation of Myostatin Knock-Out Sheep Using CRISPR/Cas9 Technology and Microinjection into Zygotes", as cited below [1]. Labome curates formal publications to compile a list of antibodies with unambiguous specificity within Validated Antibody Database (VAD).
Mouse monoclonal
Company: Santa Cruz Biotechnology
Antibody: Myostatin / GDF-8
Catalog number: sc-398333
Summary: Mouse monoclonal antibody. Recognises an epitope within residues 258-270 of myostatin. Supplier recommended for WB, IP, IF and elisa. Reacts with human, mouse, rat, bird, horse, dog, pig and cow myostatin.
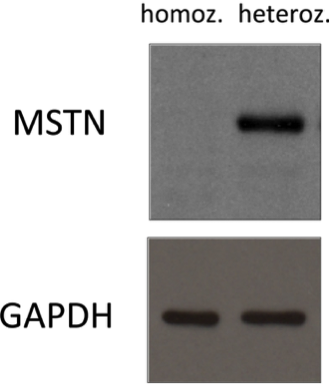
Western blot
Muscle lysates from lams homozygous and heterozygous for deletion of the myostatin gene.
Anti-myostatin antibody.
HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG diluted 1:50000.
Chemiluminescence reagent (Promega).
If the antibody described in this summary is a polyclonal antibody, since polyclonal antibodies are of limited quantity, please inquire the supplier whether any current polyclonal antibody with the same catalog number is exactly the same as the one described in this summary. Sometimes, different bleeds or different animals are used, usually with a different lot number. In such cases, the result in this summary may not apply to the new antibody with the same catalog number.
- If you are aware of any publication with knockout studies validating a monoclonal or recombinant antibody, either purchased from a supplier or developed by the author(s), please notify us through feedback.
