This is a knockout-validated antibody summary, based on the publication "Fibrinogen-like protein 2 aggravates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via interaction with TLR4, eliciting inflammation in macrophages and inducing hepatic lipid metabolism disorder", as cited below [1]. Labome curates formal publications to compile a list of antibodies with unambiguous specificity within Validated Antibody Database (VAD).
Mouse monoclonal IgG2a Kappa
Company: Abnova
Antibody: FGL2
Catalog number: H00010875-M01
Summary: Mouse monoclonal antibody raised against a partial recombinant FGL2. Reacts with human, mouse and rat. Suitable for western blot, immunohistochemistry (paraffin), immunoprecipitation, and ELISA.
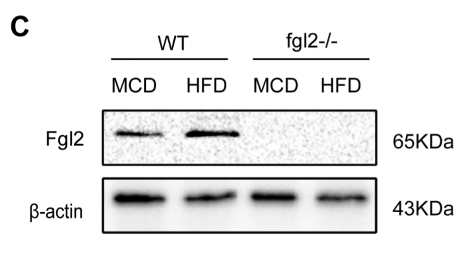
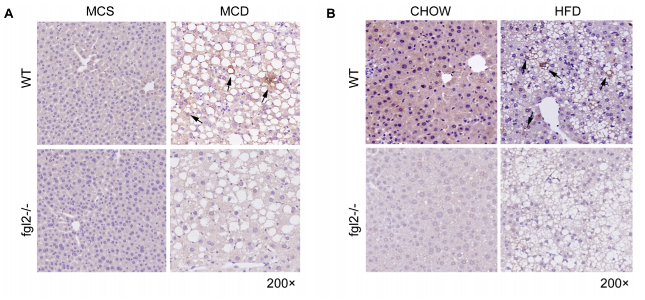
Immunohistochemistry | Western blot
WT and fgl2-/- mouse livers.
WB: 5% milk.
WB: 1:1,000 dilution.
IHC: 1:100 dilution.
WB: 1:5,000 dilution HRP goat anti-mouse IgG (A21010, Abbkine, USA).
WB: Enhanced chemiluminescence system (ChemiDoc XRS+, Bio-Rad, USA).
The same clone (6D9) is sold as MilliporeSigma WH0010875M1; LifeSpan Biosciences LS-C105107; Abnova H00010875-M01.
- If you are aware of any publication with knockout studies validating a monoclonal or recombinant antibody, either purchased from a supplier or developed by the author(s), please notify us through feedback.
