product summary
Loading...
company name :
Invitrogen
other brands :
NeoMarkers, Lab Vision, Endogen, Pierce, BioSource International, Zymed Laboratories, Caltag, Molecular Probes, Research Genetics, Life Technologies, Applied Biosystems, GIBCO BRL, ABgene, Dynal, Affinity BioReagents, Nunc, Invitrogen, NatuTec, Oxoid, Richard-Allan Scientific, Arcturus, Perseptive Biosystems, Proxeon, eBioscience
product type :
antibody
product name :
NFATC1 Monoclonal Antibody (7A6)
catalog :
MA3-024
quantity :
100 µL
price :
US 412.00
clonality :
monoclonal
host :
mouse
conjugate :
nonconjugated
clone name :
7A6
reactivity :
human, mouse, rat, domestic rabbit
application :
western blot, immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, immunoprecipitation, EMSA, chromatin immunoprecipitation, immunohistochemistry - paraffin section
more info or order :
citations: 82
| Published Application/Species/Sample/Dilution | Reference |
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Kundumani Sridharan V, Singh N, Kumar S, Gadepalli R, Rao G. Nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 mediates p21-activated kinase 1 activation in the modulation of chemokine-induced human aortic smooth muscle cell F-actin stress fiber formation, migration, and proliferation and injury-induced vascular wall rem. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:22150-62 pubmed publisher
|
| |
| |
| |
| Singh N, Kundumani Sridharan V, Kumar S, Verma S, Kotla S, Mukai H, et al. Protein kinase N1 is a novel substrate of NFATc1-mediated cyclin D1-CDK6 activity and modulates vascular smooth muscle cell division and migration leading to inward blood vessel wall remodeling. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:36291-304 pubmed publisher
|
| |
| Kundumani Sridharan V, Van Quyen D, Subramani J, Singh N, Chin Y, Rao G. Novel interactions between NFATc1 (Nuclear Factor of Activated T cells c1) and STAT-3 (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription-3) mediate G protein-coupled receptor agonist, thrombin-induced biphasic expression of cyclin D1, with first phase. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:22463-82 pubmed publisher
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Nakazato K, Song H. Increased oxidative properties of gastrocnemius in rats fed on a high-protein diet. J Nutr Biochem. 2008;19:26-32 pubmed
|
| Miyazaki M, Hitomi Y, Kizaki T, Ohno H, Katsumura T, Haga S, et al. Calcineurin-mediated slow-type fiber expression and growth in reloading condition. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006;38:1065-72 pubmed
|
| Pfeifhofer C, Gruber T, Letschka T, Thuille N, Lutz Nicoladoni C, Hermann Kleiter N, et al. Defective IgG2a/2b class switching in PKC alpha-/- mice. J Immunol. 2006;176:6004-11 pubmed
|
| Larrieu D, Thiebaud P, Duplaa C, Sibon I, Theze N, Lamazière J. Activation of the Ca(2+)/calcineurin/NFAT2 pathway controls smooth muscle cell differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 2005;310:166-75 pubmed
|
| Kaplan B, Ouyang Y, Rockwell C, Rao G, Kaminski N. 2-Arachidonoyl-glycerol suppresses interferon-gamma production in phorbol ester/ionomycin-activated mouse splenocytes independent of CB1 or CB2. J Leukoc Biol. 2005;77:966-74 pubmed
|
| De Arcangelis V, Coletti D, Canato M, Molinaro M, Adamo S, Reggiani C, et al. Hypertrophy and transcriptional regulation induced in myogenic cell line L6-C5 by an increase of extracellular calcium. J Cell Physiol. 2005;202:787-95 pubmed
|
Govatati S, Pichavaram P, Janjanam J, Guo L, Virmani R, Rao G. Myristoylation of LMCD1 Leads to Its Species-Specific Derepression of E2F1 and NFATc1 in the Modulation of CDC6 and IL-33 Expression During Development of Vascular Lesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020;40:1256-1274 pubmed publisher
| |
Wu W, Misra R, Russell J, Flavell R, Rincon M, Budd R. Proteolytic regulation of nuclear factor of activated T (NFAT) c2 cells and NFAT activity by caspase-3. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:10682-90 pubmed
| |
Shen T, Liu Y, Cseresnyes Z, Hawkins A, Randall W, Schneider M. Activity- and calcineurin-independent nuclear shuttling of NFATc1, but not NFATc3, in adult skeletal muscle fibers. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:1570-82 pubmed
| |
Scicchitano B, Spath L, Musaro A, Molinaro M, Rosenthal N, Nervi C, et al. Vasopressin-dependent myogenic cell differentiation is mediated by both Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase and calcineurin pathways. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16:3632-41 pubmed
| |
Kim H, Korn L, Gamero A, Leonard W. Calcium-dependent activation of interleukin-21 gene expression in T cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:25291-7 pubmed
| |
Liu Z, Zhang C, Dronadula N, Li Q, Rao G. Blockade of nuclear factor of activated T cells activation signaling suppresses balloon injury-induced neointima formation in a rat carotid artery model. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:14700-8 pubmed
| |
Miyazaki M, Hitomi Y, Kizaki T, Ohno H, Haga S, Takemasa T. Contribution of the calcineurin signaling pathway to overload-induced skeletal muscle fiber-type transition. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2004;55:751-64 pubmed
| |
Minami T, Horiuchi K, Miura M, Abid M, Takabe W, Noguchi N, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor- and thrombin-induced termination factor, Down syndrome critical region-1, attenuates endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:50537-54 pubmed
| |
Barlic J, McDermott D, Merrell M, Gonzales J, Via L, Murphy P. Interleukin (IL)-15 and IL-2 reciprocally regulate expression of the chemokine receptor CX3CR1 through selective NFAT1- and NFAT2-dependent mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:48520-34 pubmed
| |
Cannon J, Burkhardt J. Differential roles for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein in immune synapse formation and IL-2 production. J Immunol. 2004;173:1658-62 pubmed
| |
McCullagh K, Calabria E, Pallafacchina G, Ciciliot S, Serrano A, Argentini C, et al. NFAT is a nerve activity sensor in skeletal muscle and controls activity-dependent myosin switching. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:10590-5 pubmed
| |
Frazer Abel A, Baksh S, Fosmire S, Willis D, Pierce A, Meylemans H, et al. Nicotine activates nuclear factor of activated T cells c2 (NFATc2) and prevents cell cycle entry in T cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;311:758-69 pubmed
| |
Monticelli S, Solymar D, Rao A. Role of NFAT proteins in IL13 gene transcription in mast cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:36210-8 pubmed
| |
Rosenberg P, Hawkins A, Stiber J, Shelton J, Hutcheson K, Bassel Duby R, et al. TRPC3 channels confer cellular memory of recent neuromuscular activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:9387-92 pubmed
| |
Pfeifhofer C, Kofler K, Gruber T, Tabrizi N, Lutz C, Maly K, et al. Protein kinase C theta affects Ca2+ mobilization and NFAT cell activation in primary mouse T cells. J Exp Med. 2003;197:1525-35 pubmed
| |
Yellaturu C, Ghosh S, Rao R, Jennings L, Hassid A, Rao G. A potential role for nuclear factor of activated T-cells in receptor tyrosine kinase and G-protein-coupled receptor agonist-induced cell proliferation. Biochem J. 2002;368:183-90 pubmed
| |
Diehl S, Chow C, Weiss L, Palmetshofer A, Twardzik T, Rounds L, et al. Induction of NFATc2 expression by interleukin 6 promotes T helper type 2 differentiation. J Exp Med. 2002;196:39-49 pubmed
| |
Kim H, Leonard W. The basis for TCR-mediated regulation of the IL-2 receptor alpha chain gene: role of widely separated regulatory elements. EMBO J. 2002;21:3051-9 pubmed
| |
Dupont Versteegden E, Knox M, Gurley C, Houle J, Peterson C. Maintenance of muscle mass is not dependent on the calcineurin-NFAT pathway. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;282:C1387-95 pubmed
| |
Jan T, Rao G, Kaminski N. Cannabinol enhancement of interleukin-2 (IL-2) expression by T cells is associated with an increase in IL-2 distal nuclear factor of activated T cell activity. Mol Pharmacol. 2002;61:446-54 pubmed
| |
Kehoe K, Brown M, Imani F. Double-stranded RNA regulates IL-4 expression. J Immunol. 2001;167:2496-501 pubmed
| |
Mukerjee N, McGinnis K, Gnegy M, Wang K. Caspase-mediated calcineurin activation contributes to IL-2 release during T cell activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;285:1192-9 pubmed
| |
Keen J, Sholl L, Wills Karp M, Georas S. Preferential activation of nuclear factor of activated T cells c correlates with mouse strain susceptibility to allergic responses and interleukin-4 gene expression. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001;24:58-65 pubmed
| |
Swoap S, Hunter R, Stevenson E, Felton H, Kansagra N, Lang J, et al. The calcineurin-NFAT pathway and muscle fiber-type gene expression. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2000;279:C915-24 pubmed
| |
Chow C, Dong C, Flavell R, Davis R. c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase inhibits targeting of the protein phosphatase calcineurin to NFATc1. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:5227-34 pubmed
| |
Chen R, Burke T, Cumberland J, Brummet M, Beck L, Casolaro V, et al. Glucocorticoids inhibit calcium- and calcineurin-dependent activation of the human IL-4 promoter. J Immunol. 2000;164:825-32 pubmed
| |
Wierenga E, Walchner M, Kick G, Kapsenberg M, Weiss E, Messer G. Evidence for suppressed activity of the transcription factor NFAT1 at its proximal binding element P0 in the IL-4 promoter associated with enhanced IL-4 gene transcription in T cells of atopic patients. Int Immunol. 1999;11:297-306 pubmed
| |
Li Weber M, Giasi M, Krammer P. Involvement of Jun and Rel proteins in up-regulation of interleukin-4 gene activity by the T cell accessory molecule CD28. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:32460-6 pubmed
| |
Abbott K, Friday B, Thaloor D, Murphy T, Pavlath G. Activation and cellular localization of the cyclosporine A-sensitive transcription factor NF-AT in skeletal muscle cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1998;9:2905-16 pubmed
| |
Boss V, Wang X, Koppelman L, Xu K, Murphy T. Histamine induces nuclear factor of activated T cell-mediated transcription and cyclosporin A-sensitive interleukin-8 mRNA expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1998;54:264-72 pubmed
| |
Li Weber M, Salgame P, Hu C, Davydov I, Laur O, Klevenz S, et al. Th2-specific protein/DNA interactions at the proximal nuclear factor-AT site contribute to the functional activity of the human IL-4 promoter. J Immunol. 1998;161:1380-9 pubmed
| |
Boss V, Abbott K, Wang X, Pavlath G, Murphy T. The cyclosporin A-sensitive nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) proteins are expressed in vascular smooth muscle cells. Differential localization of NFAT isoforms and induction of NFAT-mediated transcription by phospholipase C-coupled cell sur. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:19664-71 pubmed
| |
Latinis K, Norian L, Eliason S, Koretzky G. Two NFAT transcription factor binding sites participate in the regulation of CD95 (Fas) ligand expression in activated human T cells. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:31427-34 pubmed
| |
Chow C, Rincon M, Cavanagh J, Dickens M, Davis R. Nuclear accumulation of NFAT4 opposed by the JNK signal transduction pathway. Science. 1997;278:1638-41 pubmed
| |
Lyakh L, Ghosh P, Rice N. Expression of NFAT-family proteins in normal human T cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1997;17:2475-84 pubmed
| |
Northrop J, Ho S, Chen L, Thomas D, Timmerman L, Nolan G, et al. NF-AT components define a family of transcription factors targeted in T-cell activation. Nature. 1994;369:497-502 pubmed
| |
Ho S, Thomas D, Timmerman L, Li X, Francke U, Crabtree G. NFATc3, a lymphoid-specific NFATc family member that is calcium-regulated and exhibits distinct DNA binding specificity. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:19898-907 pubmed
|
image
image 1 :
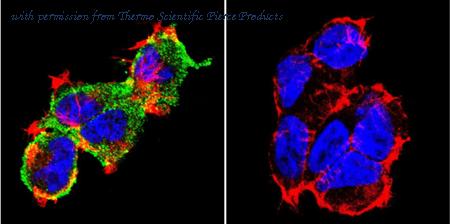
Immunofluorescent analysis of NFATc1 using NFATc1 Monoclonal Antibody (7A6) (Product# MA3-024 ) shows staining in 293Cells. NFATc1 (green), F-Actin staining with Phalloidin (red) and nuclei with DAPI (blue) is shown. Cells were grown on chamber slides and fixed with formaldehyde prior to staining. Cells were probed without (control) or with an antibody recognizing NFATc1 (Product# MA3-024 ) at a dilution of 1:20 over night at 4 ?C, washed with PBS and incubated with a DyLight-488 conjugated secondary antibody (Product# 35552 for GAR, Product# 35503 for GAM). Images were taken at 60X magnification.
image 2 :
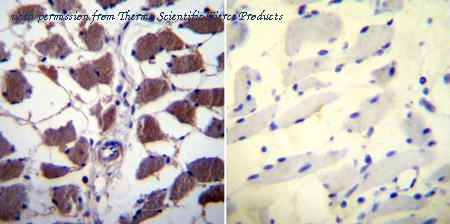
Immunohistochemistry was performed on normal biopsies of deparaffinized Human skeletal muscle tissue. To expose target proteins, heat induced antigen retrieval was performed using 10mM sodium citrate (pH6.0) buffer, microwaved for 8-15 minutes. Following antigen retrieval tissues were blocked in 3% BSA-PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Tissues were then probed at a dilution of 1:20 with a mouse monoclonal antibody recognizing NFATc1 (MA3-024) or without primary antibody (negative control) overnight at 4°C in a humidified chamber. Tissues were washed extensively with PBST and endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched with a peroxidase suppressor. Detection was performed using a biotin-conjugated secondary antibody and SA-HRP, followed by colorimetric detection using DAB. Tissues were counterstained with hematoxylin and prepped for mounting.
product information
Product Type :
Antibody
Product Name :
NFATC1 Monoclonal Antibody (7A6)
Catalog # :
MA3-024
Quantity :
100 µL
Price :
US 412.00
Clonality :
Monoclonal
Host :
Mouse
Reactivity :
Human, Mouse, Non-human primate, Rat
Applications :
ChIP assay: Assay-dependent, Gel Shift: Assay-dependent, Immunocytochemistry: 1:250, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin): Assay-dependent, Immunohistochemistry (PFA fixed): Assay-dependent, Immunoprecipitation: Assay-dependent, Western Blot: 1:2,000
Species :
Human, Mouse, Non-human primate, Rat
Clone :
7A6
Isotype :
IgG1
Storage :
-20° C, Avoid Freeze/Thaw Cycles
Description :
The product of this gene is a component of the nuclear factor of activated T cells DNA-binding transcription complex. This complex consists of at least two components: a preexisting cytosolic component that translocates to the nucleus upon T cell receptor (TCR) stimulation, and an inducible nuclear component. Proteins belonging to this family of transcription factors play a central role in inducible gene transcription during immune response. The product of this gene is an inducible nuclear component. It functions as a major molecular target for the immunosuppressive drugs such as cyclosporin A. Five transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been identified for this gene. Different isoforms of this protein may regulate inducible expression of different cytokine genes.
Immunogen :
Bacterially expressed glutathione S-transferase (GST) fusion protein containing NF-ATc1 residues 1-654.
Format :
Liquid
Applications w/Dilutions :
ChIP assay: Assay-dependent, Gel Shift: Assay-dependent, Immunocytochemistry: 1:250, Immunohistochemistry (Paraffin): Assay-dependent, Immunohistochemistry (PFA fixed): Assay-dependent, Immunoprecipitation: Assay-dependent, Western Blot: 1:2,000
Aliases :
2210017P03Rik; AI449492; AV076380; MGC138448; NFAT tra; NFAT trans; NFAT transcription complex cytosolic component; NFAT2; NFATc; NF-ATC; NFATC1; NF-ATc1; NF-ATc1.2; Nfatcb; nuclear factor of activated T cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin dependent 1; nuclear factor of activated T-cells 1; nuclear factor of activated T-cells 'c'; nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1; nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent 1; transcription factor NF-ATc
more info or order :
company information

Invitrogen
Thermo Fisher Scientific
81 Wyman Street
Waltham, MA USA 02451
https://www.thermofisher.com81 Wyman Street
Waltham, MA USA 02451
800-678-5599
headquarters: USA
related products
browse more products
questions and comments
