product summary
Loading...
company name :
Alomone Labs
product type :
chemical
product name :
α-Latrotoxin
catalog :
LSP-130
more info or order :
citations: 24
| Reference |
|---|
Vezain M, Lecuyer M, Rubio M, Dupé V, Ratié L, David V, et al. A de novo variant in ADGRL2 suggests a novel mechanism underlying the previously undescribed association of extreme microcephaly with severely reduced sulcation and rhombencephalosynapsis. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018;6:109 pubmed publisher
|
Arunachalam L, Han L, Tassew N, He Y, Wang L, Xie L, et al. Munc18-1 is critical for plasma membrane localization of syntaxin1 but not of SNAP-25 in PC12 cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2008;19:722-34 pubmed
|
Rohou A, Nield J, Ushkaryov Y. Insecticidal toxins from black widow spider venom. Toxicon. 2007;49:531-49 pubmed
|
Blair D, Lin Y, Bennett M. Differential sensitivity to calcium and osmotic pressure of fast and slow ATP currents at sympathetic varicosities in mouse vas deferens. Auton Neurosci. 2003;105:45-52 pubmed
|
Bullens R, O Hanlon G, Wagner E, Molenaar P, Furukawa K, Furukawa K, et al. Complex gangliosides at the neuromuscular junction are membrane receptors for autoantibodies and botulinum neurotoxin but redundant for normal synaptic function. J Neurosci. 2002;22:6876-84 pubmed
|
Zygmunt P, Andersson D, Hogestatt E. Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabinol activate capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves via a CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptor-independent mechanism. J Neurosci. 2002;22:4720-7 pubmed
|
Zygmunt P, Petersson J, Andersson D, Chuang H, Sørgård M, Di Marzo V, et al. Vanilloid receptors on sensory nerves mediate the vasodilator action of anandamide. Nature. 1999;400:452-7 pubmed
|
Plomp J, Molenaar P, O Hanlon G, Jacobs B, Veitch J, Daha M, et al. Miller Fisher anti-GQ1b antibodies: alpha-latrotoxin-like effects on motor end plates. Ann Neurol. 1999;45:189-99 pubmed
|
Boehm S, Huck S. Presynaptic inhibition by concanavalin A: are alpha-latrotoxin receptors involved in action potential-dependent transmitter release?. J Neurochem. 1998;71:2421-30 pubmed
|
Nakata T, Terada S, Hirokawa N. Visualization of the dynamics of synaptic vesicle and plasma membrane proteins in living axons. J Cell Biol. 1998;140:659-74 pubmed
|
De Potter W, Partoens P, Schoups A, Llona I, Coen E. Noradrenergic neurons release both noradrenaline and neuropeptide Y from a single pool: the large dense cored vesicles. Synapse. 1997;25:44-55 pubmed
|
Boehm S, Huck S. Inhibition of N-type calcium channels: the only mechanism by which presynaptic alpha 2-autoreceptors control sympathetic transmitter release. Eur J Neurosci. 1996;8:1924-31 pubmed
|
Waterman S, Maggi C. Stimulation of neuropeptide release from sensory and enteric neurons in the guinea-pig by alpha-latrotoxin. Neuroscience. 1995;69:977-84 pubmed
|
image
image 1 :
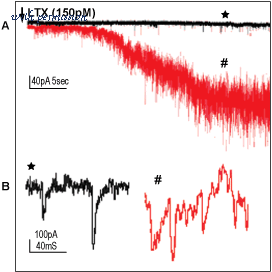
Alomone Labs ?-Latrotoxinelicits synaptic transmission. - A. Superimposed current traces of post synaptic recording from dissociatedhippocampal neurons in culture before (black) and after (red) application of ?-Latrotoxin (#LSP-130). B. Individual post synaptic currents are magnified from A.
image 2 :
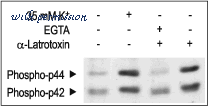
Alomone Labs ?-Latrotoxin activates P42/44 MAP kinase by inducing Ca2+influx in RIN insulinoma cells. - Cells were treated for 15 min with 35 mM K+or 2 nM?-Latrotoxin(#LSP-130) in the presence or absence of 5 mM EGTA. Cell proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and probed with anti-phospho-P42/44 antibodies.
product information
cat :
LSP-130
SKU :
LSP-130_0.2 mg
Product Name :
α-Latrotoxin
Group Type :
Non Antibodies
Product Type :
Proteins
Accession :
P23631
Accession Number :
https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P23631/entry
Applications :
Electrophysiology, Synaptic recording
Formulation :
Lyopholized in 20mM KPO4 pH 6.8.
Storage After Reconstitution :
Store the reconstituted solution for the shortest time possible at -20°C. We do not recommend storing the product in working solution for longer than one day. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles.
Reconstitution and Solubility :
Centrifuge the vial (10,000 × g for 5 minutes) before adding solvent to spin down all the powder to the bottom of the vial. The lyophilized product may be difficult to visualize. Add solvent directly to the centrifuged vial. Gently tap, tilt, and roll the vial to aid dissolution. Avoid vigorous vortexing; light vortexing for up to 3 seconds is acceptable if needed. Soluble in water. Once dissolved in water, add an equal volume of glycerol. Do not shake or vortex. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles to maintain biological activity.
Solubility :
Centrifuge the vial before adding solvent (10,000 x g for 5 minutes) to spin down all the powder to the bottom of the vial. The lyophilized product may be difficult to visualize. Add solvent directly to the centrifuged vial. Tap the vial to aid in dissolving the lyophilized product. Tilt and gently roll the liquid over the walls of the vial. Avoid vigorous vortexing. Light vortexing for up to 3 seconds is acceptable if needed. Soluble in water. Once dissolved in water, add an equal volume of glycerol. Do not shake or vortex. Avoid multiple freeze-thawing cycles.
Storage Before Reconstitution :
The product is shipped as a lyophilized powder at room temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at -20°C. Protect from moisture.
Origin :
Latrodectus tredecimguttatus (Mediterranean black widow spider).
Source :
Natural protein
Gene ID :
ADGRL1,NRXN1,PTPRS
Product Page - Scientific background :
α-Latrotoxin is a 130 kDa protein toxin from the black widow spider venom and is the only protein in the venom that affects mammals.1,2 Application of the toxin to presynaptic preparations induces, after a delay, a huge increase in spontaneous neurotransmitter release, which can be evaluated by measuring the post synaptic response in the form of miniature end plate potentials. This toxin is widely used to induce and study neurotransmitter release, but the molecular mechanism of its action is not fully determined.α-Latrotoxin is isolated according to a modified protocol as described by Frontali3 and Grasso4.
Supplier :
Alomone Labs
Target :
Neurexin-1, ADGRL1 (latrophilin-1/CIRL), and tyrosine-protein phosphatase S (PTPRS) receptors
Long Description :
An Inducer of Neurotransmitter Release
Short Description :
An Inducer of Neurotransmitter Release
MW :
130 kDa
Synonyms :
α-Latrotoxin-Lt1a, α-LTX-Lt1a, α-LTX
Modifications :
Highly disulfide bridged protein Glycosylated
Effective Concentration :
150 pM - 1 nM
Activity :
α-Latrotoxin induces exhaustive neurotransmitter release from nerve terminals1. Indirectly activates the ERK MAP kinase pathway.
Storage of solutions :
The reconstituted solution can be stored at 4°C for up to 1 week. For longer periods (up to 6 months), small aliquots should be stored at -20°C. We do not recommend storing the product in working solutions for longer than a few days. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles.
Lead Time :
1-2 Business Days
Country of origin :
Israel/IL
Purity :
≥98% (HPLC)
CAS No :
65988-34-3
Form :
Lyophilized
Comment :
Contact Alomone Labs for technical support and product customization
Is Toxin :
Yes
UNSPSC :
12352202
Bioassay Tested :
yes
Steril endotoxin free :
yes
more info or order :
company information

Alomone Labs
Jerusalem BioPark (JBP), Hadassah Ein Kerem
P.O. Box 4287
Jerusalem 9104201
P.O. Box 4287
Jerusalem 9104201
info@alomone.com
http://www.alomone.com972 2 531 8002
headquarters: Israel
browse more products
questions and comments
