product summary
Loading...
company name :
Alomone Labs
product type :
chemical
product name :
Dendrotoxin-K
catalog :
D-400
more info or order :
citations: 26
| Reference |
|---|
Fellerhoff Losch B, Korol S, Ganor Y, Gu S, Cooper I, Eilam R, et al. Normal human CD4(+) helper T cells express Kv1.1 voltage-gated K(+) channels, and selective Kv1.1 block in T cells induces by itself robust TNFα production and secretion and activation of the NFκB non-canonical pathway. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2016;123:137-57 pubmed publisher
|
Yang Q, Chen S, Li D, Pan H. Kv1.1/1.2 channels are downstream effectors of nitric oxide on synaptic GABA release to preautonomic neurons in the paraventricular nucleus. Neuroscience. 2007;149:315-27 pubmed
|
Guan D, Lee J, Tkatch T, Surmeier D, Armstrong W, Foehring R. Expression and biophysical properties of Kv1 channels in supragranular neocortical pyramidal neurones. J Physiol. 2006;571:371-89 pubmed
|
Speake T, Kibble J, Brown P. Kv1.1 and Kv1.3 channels contribute to the delayed-rectifying K+ conductance in rat choroid plexus epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004;286:C611-20 pubmed
|
Liu Q, Fleischmann B, Hondowicz B, Maier C, Turka L, Yui K, et al. Modulation of Kv channel expression and function by TCR and costimulatory signals during peripheral CD4(+) lymphocyte differentiation. J Exp Med. 2002;196:897-909 pubmed
|
image
image 1 :
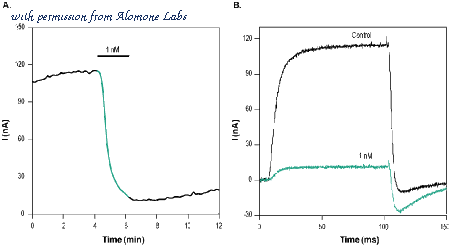
Alomone Labs Dendrotoxin-K inhibits KV1.1 channel currents heterologously expressed inXenopusoocytes. - A. Time course at plateau ofDendrotoxin-K(#D-400) action on KV1.1 currents. Current amplitude at plateau was plotted as a function of time. Membrane potential was held at -80 mV and oocytes were stimulated by a 100 ms voltage ramp to -10 mV. 1 nM Dendrotoxin-K (applied for 2 min green) were perfused during the period marked by the bar (as indicated) and showed 70-80% inhibition of control current. B. Superimposed traces of channel current in the absence (black) and presence (green) of 1 nM Dendrotoxin-K (taken from experiment in A).
image 2 :
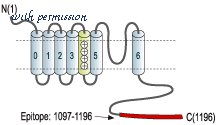
GST fusion protein with the sequence SHSSHSSQSSSKKSSSVHSIPSTANRPNRPKSRESRDKQNATRMTRMGQAEKKWFTDEPDNAYPRNIQIKPMSTHMANQINQYKSTSSLIPPIREVEDEC corresponding to residues 1097-1196 of mouse KCNMA1variant 2 (AccessionQ08460-2). Intracellular C-terminus.
product information
cat :
D-400
SKU :
D-400_10 mcg
Product Name :
Dendrotoxin-K
Group Type :
Non Antibodies
Product Type :
Proteins
Accession :
P00981
Accession Number :
https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P00981/entry
Applications :
Electrophysiology
Formulation :
Lyophilized from double distilled water (ddH2O). May contain TFA as a residual counter ion.
Storage After Reconstitution :
The reconstituted solution can be stored at 4°C for up to 1 week. For longer periods (up to 6 months), small aliquots should be stored at -20°C. We do not recommend storing the product in working solutions for longer than a few days. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles.
Reconstitution and Solubility :
Centrifuge the vial (10,000 × g for 5 minutes) before adding solvent to spin down all the powder to the bottom of the vial. The lyophilized product may be difficult to visualize. Add solvent directly to the centrifuged vial. Gently tap, tilt, and roll the vial to aid dissolution. Avoid vigorous vortexing; light vortexing for up to 3 seconds is acceptable if needed. The product is soluble in pure water at high micromolar concentrations (100 µM - 1 mM). For long-term storage in solution, we recommend preparing a stock solution by dissolving the product in double-distilled water (ddH2O) at a concentration between 100-1000x of the final working concentration. Divide the stock solution into small aliquots and store at -20°C. Before use, thaw the relevant vial(s) and dilute to the desired working concentration in your working buffer. Centrifuge all product preparations before use. It is recommended to prepare fresh solutions in working buffers just before use. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles to maintain biological activity.
Solubility :
Centrifuge the vial before adding solvent (10,000 x g for 5 minutes) to spin down all the powder to the bottom of the vial. The lyophilized product may be difficult to visualize. Add solvent directly to the centrifuged vial. Tap the vial to aid in dissolving the lyophilized product. Tilt and gently roll the liquid over the walls of the vial. Avoid vigorous vortexing. Light vortexing for up to 3 seconds is acceptable if needed. The product is soluble in pure water at high micromolar concentrations (100 µM - 1 mM). For long-term storage in solution, we recommend preparing a stock solution by dissolving the product in double-distilled water (ddH2O) at a concentration between 100-1000x of the final working concentration. Divide the stock solution into small aliquots and store at -20°C. Before use, thaw the relevant vial(s) and dilute to the desired working concentration in your working buffer. Centrifuge all product preparations before use. It is recommended to prepare fresh solutions in working buffers just before use. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles to maintain biological activity.
Storage Before Reconstitution :
The product is shipped as a lyophilized powder at room temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at -20°C. Protect from moisture.
Origin :
Dendroaspis polylepis polylepis (Black mamba snake).
Source :
Natural protein
Gene ID :
KCNA1
Product Page - Scientific background :
Dendrotoxin-K is isolated from Dendroaspis p.polylepis snake venom by modification of the procedure of Schweitz1 and purified to homogeneity. It blocks mainly KV1.1 (EC50=0.6 nM2) and Kv1.1-containing heterooligomer.
Supplier :
Alomone Labs
Target :
KV1.1, Kv1.1-containing heterooligomer.
Long Description :
A Potent Blocker of KV1.1 and KV1.2 Channels
Short Description :
A Potent Blocker of KV1.1 and KV1.2 Channels
MW :
6560 Da
Synonyms :
Venom basic protease inhibitor K, DTX-K
Modifications :
Disulfide bonds between: Cys5-Cys55, Cys14-Cys38, and Cys30-Cys51
Molecular formula :
C294H456N84O75S6
Effective Concentration :
100 nM
Activity :
Dendrotoxin-K is a highly selective and potent blocker of voltage-gated K+ channels KV1.1 and Kv1.1-containing heterooligomer.
Storage of solutions :
The reconstituted solution can be stored at 4°C for up to 1 week. For longer periods (up to 6 months), small aliquots should be stored at -20°C. We do not recommend storing the product in working solutions for longer than a few days. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles.
Lead Time :
1-2 Business Days
Country of origin :
Israel/IL
Purity :
≥99% (HPLC)
CAS No :
119128-61-9
Form :
Lyophilized
Comment :
Contact Alomone Labs for technical support and product customization
Sequence :
AAKYCKLPLRIGPCKRKIPSFYYKWKAKQCLPFDYSGCG
GNANRFKTIEECRRTCVG-OH
GNANRFKTIEECRRTCVG-OH
Is Toxin :
Yes
UNSPSC :
12352202
Bioassay Tested :
yes
Steril endotoxin free :
no
Cited Application :
Electrophysiology
more info or order :
company information

Alomone Labs
Jerusalem BioPark (JBP), Hadassah Ein Kerem
P.O. Box 4287
Jerusalem 9104201
P.O. Box 4287
Jerusalem 9104201
info@alomone.com
http://www.alomone.com972 2 531 8002
headquarters: Israel
browse more products
questions and comments
